【深度学习】深度神经网络框架的探索(从Regression说起)
1 从逻辑回归说起
2 深度学习框架
3 基于反向传播算法的自动求导
4 简单深度神经网络框架实现
4.1 数据结构
4.2 计算图组件
4.3 训练模型(部分代码)1 从逻辑回归说起
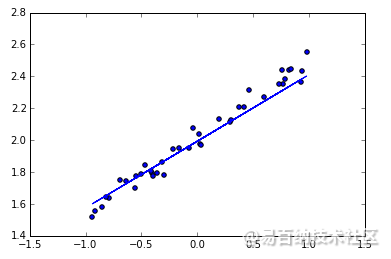
神经网络可以用来模拟回归问题 (regression),例如给下面一组数据,用一条线来对数据进行拟合,并可以预测新输入 x 的输出值。
导入模块并创建数据
models.Sequential,用来一层一层一层的去建立神经层; layers.Dense 意思是这个神经层是全连接层。

建立模型
然后用 Sequential 建立 model, 再用 model.add 添加神经层,添加的是 Dense 全连接神经层。
参数有两个,一个是输入数据和输出数据的维度,本代码的例子中 x 和 y 是一维的。
如果需要添加下一个神经层的时候,不用再定义输入的纬度,因为它默认就把前一层的输出作为当前层的输入。在这个例子里,只需要一层就够了。
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(output_dim=1, input_dim=1))
激活模型
接下来要激活神经网络,上一步只是定义模型。
参数中,误差函数用的是 mse 均方误差;优化器用的是 sgd 随机梯度下降法。
choose loss function and optimizing method
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='sgd')
以上三行就构建好了一个神经网络,它比 Tensorflow 要少了很多代码,很简单。
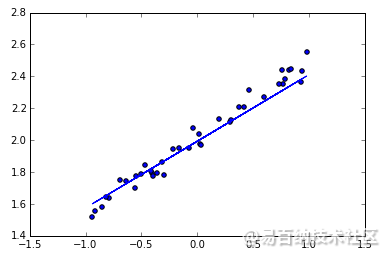
可视化结果
最后可以画出预测结果,与测试集的值进行对比。
plotting the prediction
Y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
plt.scatter(X_test, Y_test)
plt.plot(X_test, Y_pred)
plt.show()
2 深度学习框架
近几年最火的深度学习框架是什么?毫无疑问,TensorFlow 高票当选。同时Caffe、PyTorch、MXNet、CNTK用得也非常多。这些框架虽各有优势,但都具有一些普遍特征,据Gokula Krishnan Santhanam总结,大部分深度学习框架都包含以下五个核心组件:
(1)张量(Tensor) 的数据结构。
(2)基于张量的各种操作。
(3) (Computation Graph)
(4) (Automatic Differentiation)
(5) BLAS cuBLAS. cuDNN 4 tiRE.其中,张量(Tensor)可以理解为任意维度的数组一-比 如一维数组被称作向量(Vector) ,三维的被称作矩阵(Matrix) ,这些都属于张量。有了张量,就有对应的基本操作,如取某行某列的值、张量乘以常数等。运用拓展包其实就相当于使用底层计算软件加速运算。我们今天重点介绍的就是计算图模型和自动微分两部分。首先谈谈如何实现自动求导,然后用最简单的方法实现这两部分。
3 基于反向传播算法的自动求导
首先看正向传播。给定函数e= (a+ b)(b+1),当a=2、b=1时,进行正向传播,其实就是小学乘法,即将a=2、 b=1带入,e=(a+b)(b+ 1)=3x2=6。反向传播过程就麻烦一-些了.我们暂日可以将这个式子直接运用求导法则进行求导。
自动微分(Automatic Differentiation,简称AD)也称自动求导,算法能够计算可导函数在某点处的导数值的计算,是反向传播算法的一般化。自动微分要解决的核心问题是计算复杂函数,通常是多层复合函数在某一点处的导数,梯度,以及Hessian矩阵值。它对用户屏蔽了繁琐的求导细节和过程。目前知名的深度学习开源库均提供了自动微分的功能,包括TensorFlow、pytorch等。
对于编程计算目标函数的导数值,目前有4种方法:手动微分,数值微分,符号微分,以及自动微分,在接下来会分别进行介绍。
自动微分在深度学习库中的地位
自动微分技术在深度学习库中处于重要地位,是整个训练算法的核心组件之一。一个典型的深度学习库架构如下图所示。在这里忽略了网络通信,本地IO等模块。

梯度计算一般使用本文所讲述的自动微分技术,计算出梯度值给优化器使用,用于训练阶段。如果使用标准的梯度下降法进行迭代,在第k次迭代时的计算公式为

可以理解为看你和真实值差多少而已,然后反向传播,不断调整。
4 简单深度神经网络框架实现
4.1 数据结构
class Node(object):
"""
Base class for nodes in the network.
Arguments:
`inbound_nodes`: A list of nodes with edges into this node.
"""
def __init__(self, inbound_nodes=[]):
"""
Node's constructor (runs when the object is instantiated). Sets
properties that all nodes need.
"""
# A list of nodes with edges into this node.
self.inbound_nodes = inbound_nodes
# The eventual value of this node. Set by running
# the forward() method.
self.value = None
# A list of nodes that this node outputs to.
self.outbound_nodes = []
# New property! Keys are the inputs to this node and
# their values are the partials of this node with
# respect to that input.
self.gradients = {}
# Sets this node as an outbound node for all of
# this node's inputs.
for node in inbound_nodes:
node.outbound_nodes.append(self)
def forward(self):
"""
Every node that uses this class as a base class will
need to define its own `forward` method.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def backward(self):
"""
Every node that uses this class as a base class will
need to define its own `backward` method.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
class Input(Node):
"""
A generic input into the network.
"""
def __init__(self):
Node.__init__(self)
def forward(self):
pass
def backward(self):
self.gradients = {self: 0}
for n in self.outbound_nodes:
self.gradients[self] += n.gradients[self]
class Linear(Node):
"""
Represents a node that performs a linear transform.
"""
def __init__(self, X, W, b):
Node.__init__(self, [X, W, b])
def forward(self):
"""
Performs the math behind a linear transform.
"""
X = self.inbound_nodes[0].value
W = self.inbound_nodes[1].value
b = self.inbound_nodes[2].value
self.value = np.dot(X, W) + b
def backward(self):
"""
Calculates the gradient based on the output values.
"""
self.gradients = {n: np.zeros_like(n.value) for n in self.inbound_nodes}
for n in self.outbound_nodes:
grad_cost = n.gradients[self]
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] += np.dot(grad_cost, self.inbound_nodes[1].value.T)
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[1]] += np.dot(self.inbound_nodes[0].value.T, grad_cost)
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[2]] += np.sum(grad_cost, axis=0, keepdims=False)
class Sigmoid(Node):
"""
Represents a node that performs the sigmoid activation function.
"""
def __init__(self, node):
Node.__init__(self, [node])
def _sigmoid(self, x):
"""
This method is separate from `forward` because it
will be used with `backward` as well.
`x`: A numpy array-like object.
"""
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-x))
def forward(self):
"""
Perform the sigmoid function and set the value.
"""
input_value = self.inbound_nodes[0].value
self.value = self._sigmoid(input_value)
def backward(self):
"""
Calculates the gradient using the derivative of
the sigmoid function.
"""
self.gradients = {n: np.zeros_like(n.value) for n in self.inbound_nodes}
for n in self.outbound_nodes:
grad_cost = n.gradients[self]
sigmoid = self.value
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] += sigmoid * (1 - sigmoid) * grad_cost
class MSE(Node):
def __init__(self, y, a):
"""
The mean squared error cost function.
Should be used as the last node for a network.
"""
Node.__init__(self, [y, a])
def forward(self):
"""
Calculates the mean squared error.
"""
y = self.inbound_nodes[0].value.reshape(-1, 1)
a = self.inbound_nodes[1].value.reshape(-1, 1)
self.m = self.inbound_nodes[0].value.shape[0]
self.diff = y - a
self.value = np.mean(self.diff**2)
def backward(self):
"""
Calculates the gradient of the cost.
"""
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] = (2 / self.m) * self.diff
self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[1]] = (-2 / self.m) * self.diff4.2 计算图组件
源深度学习库Tensorflow通过计算图(Computational Graph)表述计算流程。学过数据结构的同学都不会对图的概念陌生。Tensorflow中的每一个数据都是计算图上的一个节点,节点之间的边描述了数据之间的计算即流向关系。下面是一个典型的计算图。
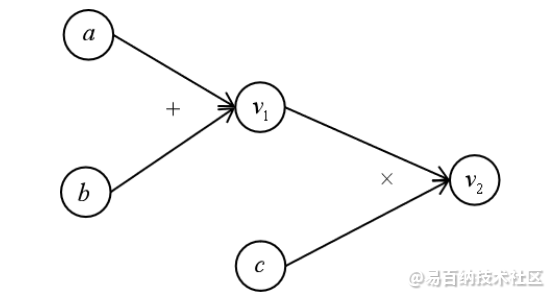
该图所表示的运算为
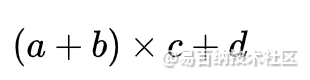
其中节点 v1,v2为表示中间结果或最终结果的变量。在后面的讲述中,将会以计算图作为工具。
# python
def topological_sort(feed_dict):
"""
Sort the nodes in topological order using Kahn's Algorithm.
`feed_dict`: A dictionary where the key is a `Input` Node and the value is the respective value feed to that Node.
Returns a list of sorted nodes.
"""
input_nodes = [n for n in feed_dict.keys()]
G = {}
nodes = [n for n in input_nodes]
while len(nodes) > 0:
n = nodes.pop(0)
if n not in G:
G[n] = {'in': set(), 'out': set()}
for m in n.outbound_nodes:
if m not in G:
G[m] = {'in': set(), 'out': set()}
G[n]['out'].add(m)
G[m]['in'].add(n)
nodes.append(m)
L = []
S = set(input_nodes)
while len(S) > 0:
n = S.pop()
if isinstance(n, Input):
n.value = feed_dict[n]
L.append(n)
for m in n.outbound_nodes:
G[n]['out'].remove(m)
G[m]['in'].remove(n)
if len(G[m]['in']) == 0:
S.add(m)
return L
4.3 训练模型(部分代码)
一个优化例子:
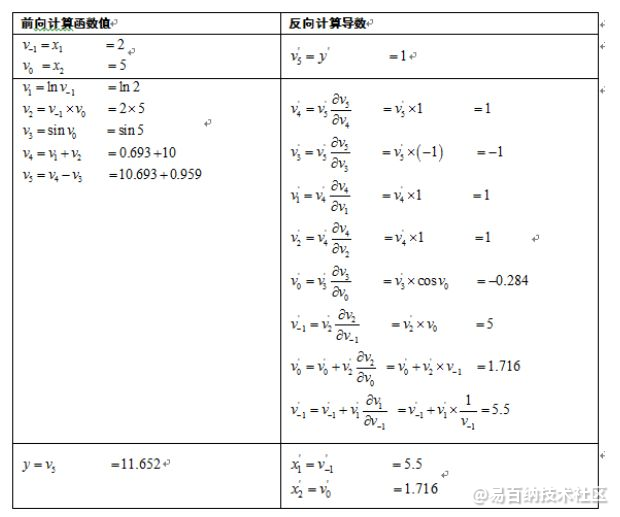
再看代码:
# 随机初始化参数值
W1_0 = np.random.random(X_.shape[1]*n_hidden).reshape([X_.shape[1], n_hidden])
W2_0 = np.random.random(n_hidden*n_class).reshape([n_hidden, n_class])
b1_0 = np.random.random(n_hidden)
b2_0 = np.random.random(n_class)
# 将输入值带入算子
feed_dict = {
X: X_, y: y_,
W1: W1_0, b1: b1_0,
W2: W2_0, b2: b2_0
}
# 训练参数
# 这里训练100轮(eprochs),每轮抽4个样本(batch_size)训练150/4次(steps_per_eproch),学习率 0.1
epochs = 100
m = X_.shape[0]
batch_size = 4
steps_per_epoch = m // batch_size
lr = 0.1
graph = topological_sort(feed_dict)
trainables = [W1, b1, W2, b2]
l_Mat_W1 = [W1_0]
l_Mat_W2 = [W2_0]
l_loss = []
for i in range(epochs):
loss = 0
for j in range(steps_per_epoch):
X_batch, y_batch = resample(X_, y_, n_samples=batch_size)
X.value = X_batch
y.value = y_batch
forward_and_backward(graph)
sgd_update(trainables, lr)
loss += graph[-1].value
l_loss.append(loss)
if i % 10 == 9:
print("Eproch %d, Loss = %1.5f" % (i, loss))
- 分享
- 举报
 暂无数据
暂无数据-
浏览量:5293次2021-04-23 14:09:37
-
浏览量:4635次2021-04-19 14:54:23
-
浏览量:4433次2018-02-14 10:30:11
-
浏览量:7117次2021-05-31 17:02:05
-
浏览量:4841次2021-04-23 14:09:15
-
浏览量:5646次2021-08-13 15:39:02
-
浏览量:6068次2021-05-28 16:59:25
-
浏览量:9123次2021-05-28 16:59:43
-
2023-01-12 11:47:40
-
浏览量:9690次2021-05-13 12:53:50
-
浏览量:946次2023-08-28 09:56:42
-
浏览量:18386次2021-06-07 17:47:54
-
浏览量:1257次2024-02-01 14:20:47
-
浏览量:4463次2021-05-14 09:47:57
-
浏览量:5207次2021-04-21 17:05:28
-
浏览量:1501次2024-02-01 14:28:23
-
浏览量:888次2023-09-28 11:44:09
-
浏览量:5404次2021-07-26 11:28:05
-
浏览量:6860次2021-07-14 09:51:09
-
广告/SPAM
-
恶意灌水
-
违规内容
-
文不对题
-
重复发帖
这把我C




 微信支付
微信支付举报类型
- 内容涉黄/赌/毒
- 内容侵权/抄袭
- 政治相关
- 涉嫌广告
- 侮辱谩骂
- 其他
详细说明


 微信扫码分享
微信扫码分享 QQ好友
QQ好友





